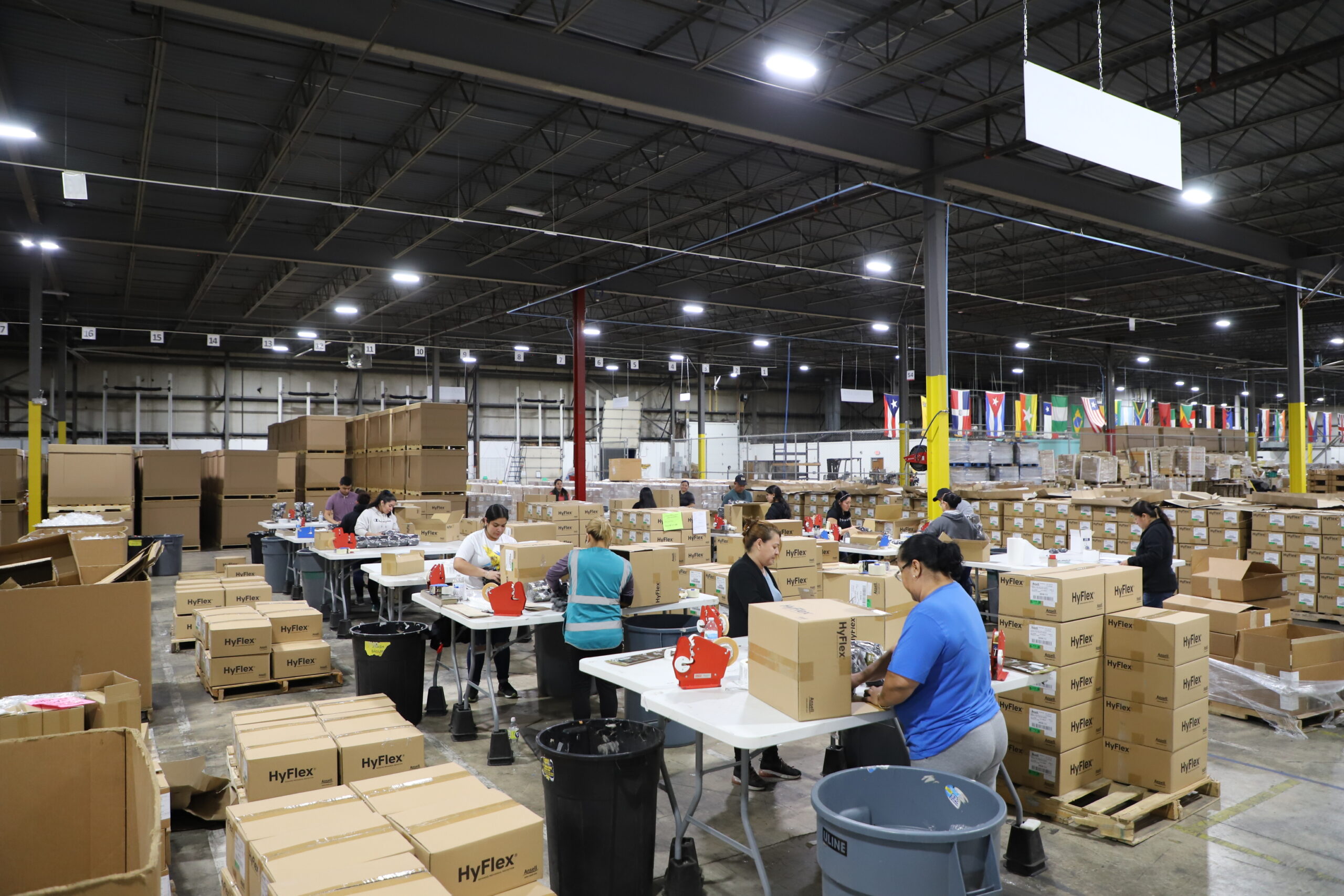
Partnering with Acción Performance allows your business to remain agile as production needs shift. Our customized Retail and Logistics Management services eliminate wasted resources by optimizing performance as we seamlessly integrate into your logistics processes.
Our Retail and Logistics Management Services



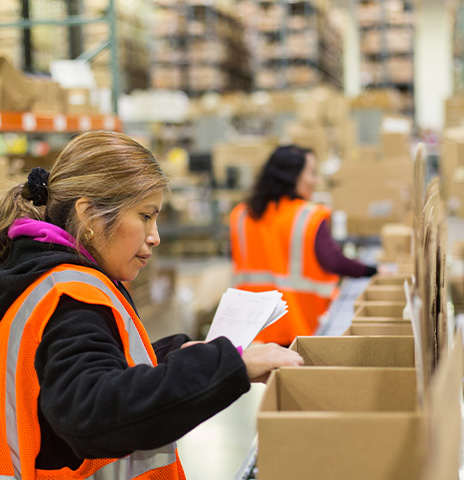
Packaging Solutions
Stay on top of product alterations and capitalize on packaging as a marketing tool to your clients. Our team can focus on product appearance while ensuring safe and secure delivery to its destination.
OUR CAPABILITIES
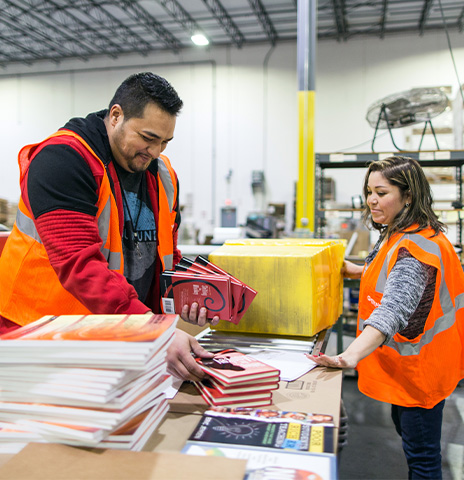



Assembly & Co-Manufacturing Solutions
Reduce overhead costs and boost speed to market by shifting your assembly and co-manufacturing tasks to the Acción team. Our skilled team prioritizes quality and safety at every step.
OUR CAPABILITIES
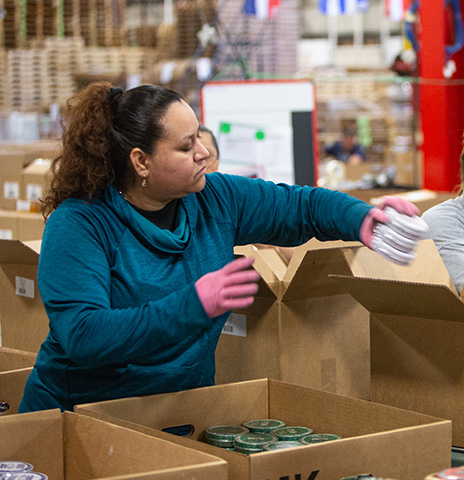
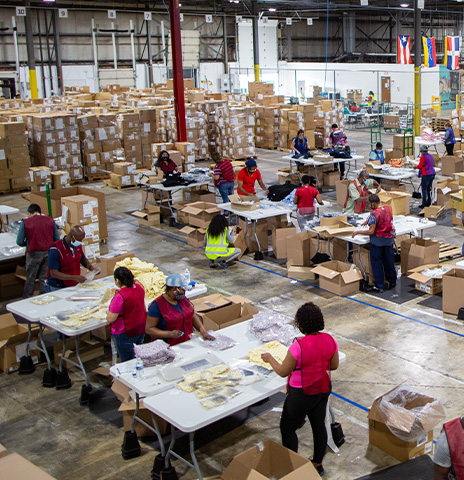



Fulfillment & Logistics Support
Improve efficiency and maintain client satisfaction by outsourcing key fulfillment operations. Our team leads will manage processes from pick and pack all the way to returns.
OUR CAPABILITIES
- Kitting and Assembly
- Primary and Secondary Packaging
- Shrink Wrap
- Labeling and Stickering
- Sortation
- Repack and Rework
- Display Builds
- Returns
- Refurbishing



Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) Prep
Ensure your products are properly packaged and sent on time for Fulfillment by Amazon. Acción Performance prepares your items to fit necessary requirements, saving your team extra time and valuable resources.
OUR CAPABILITIES
- Packaging Solutions
-



Packaging Solutions
Stay on top of product alterations and capitalize on packaging as a marketing tool to your clients. Our team can focus on product appearance while ensuring safe and secure delivery to its destination.
OUR CAPABILITIES
- Assembly &Co-Manufacturing Solutions
-



Assembly & Co-Manufacturing Solutions
Reduce overhead costs and boost speed to market by shifting your assembly and co-manufacturing tasks to the Acción team. Our skilled team prioritizes quality and safety at every step.
OUR CAPABILITIES
- Fulfillment &Logistics Support
-



Fulfillment & Logistics Support
Improve efficiency and maintain client satisfaction by outsourcing key fulfillment operations. Our team leads will manage processes from pick and pack all the way to returns.
<OUR CAPABILITIES
- Kitting and Assembly
- Primary and Secondary Packaging
- Shrink Wrap
- Labeling and Stickering
- Sortation
- Repack and Rework
- Display Builds
- Returns
- Refurbishing
- Fulfillment byAmazon (FBA) Prep
-



Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) Prep
Ensure your products are properly packaged and sent on time for Fulfillment by Amazon. Acción Performance prepares your items to fit necessary requirements, saving your team extra time and valuable resources.
OUR CAPABILITIES
Our Capabilities
Don’t let capacity constraints keep you from reaching your operational goals. Acción Performance can quickly adjust our resources to get started on projects quickly, and exceed timeline expectations.
Managing Modern Solutions
Optimized supply chain solutions aren’t “one size fits all,” and neither are our pricing models. Our team
finds the best approach for your project to maximize your resources, including cost.








Custom Solutions
See how the Acción team creates individualized solutions for our clients across industries to optimize their unique demands.
Logistics management is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, effective movement and storage of products, services, and associated information from point of origin to point of consumption in order to fulfill customer needs.
Customer service, sourcing and procurement, production planning and scheduling, packaging, and assembly are all functions of logistics management to varied degrees. Logistics management is integrated into all stages of planning and execution, including strategic, operational, and tactical planning and execution.
Additionally, logistics management control and combines all logistical activities, including marketing, sales, production, finance, and information technology.
Logistics Companies
The goal of retail logistics companies is to guarantee that the supply chain is maintained properly so that customers receive what they want, when they want. Retail logistics entail the acquisition of products, the receipt of inventories, fulfillment, and delivery. Each stage of the retail logistics process requires a plan and the appropriate systems to ensure that supply chain remains efficient and operational.
Types of Logistics Companies
Within the logistics sector as a whole, several types of logistic companies provide a variety of services. Additionally, there are businesses that specialize in specific elements of the sector, such as cold chain management and transportation. However, the logistics sector may be divided into four broad categories, majorly based on types of logistics transportation:
- Freight Companies. These are logistic companies that actually transport your items from point A to point B. They might be modest, transporting solely domestic freight, or massive, transporting international and global goods. Additionally, companies may specialize in certain means of transport, such as sea or air freight, or they may provide a combination of forms of transit.
- Freight forwarders. These companies lack any methods of freight transportation. Rather than that, they act as a facilitator inside the supply chain, utilizing their established networks to enhance your logistics transportation options. Along with organizing the shipment of your products, they will take care of all documentation, including import and export papers. These organizations will have extensive knowledge and a network of carrier partners, which will enable them to save you time and money in the short and long term.
- Carriers. These firms will handle your shipments directly. Rail firms, air cargo companies, and ocean freight corporations are all examples of these.
- Third-party logistics companies. Often referred to as 3PLs, these are logistics companies that specialize in supplying all or a portion of the logistics for your business’s supply chain. How much of that chain they supply is entirely dependent on the customer’s requirements. They may provide merely transportation and storage services, or they may be an integral element of your complete company strategy, including warehousing, order picking, packing, management ordering, and delivery services.
Types of logistics in supply chain management, also types of logistics management, are classified into four broad categories: supply, distribution, production, and reverse logistics. Each kind is devoted to a certain part of the supply chain.
There are 3 types of logistics: inbound logistics, outbound logistics, and reverse logistics. The knowledge of these three supply chain directions is critical for anybody involved in the logistics sector.
A manufacturer or business can handle logistics in a variety of ways. Some have their own fleet of cars, while others completely outsource the transportation and handling of their goods. Listed below are some types of logistics models.
- 1PL- Self Logistics: 1PL or first-party logistics refers to a manufacturer or business that has their cargo, freight, or other commodities transported from one location to another. In other words, this approach applies to businesses and merchants that are self-sufficient in terms of administering and managing transportation. The corporation or trader in this case is the consignor, who oversees the entire shipping procedure in its entirety.
- 2PL- Traditional Transportation Provider: This logistic model simply refers to the middleman between buyer and seller, i.e. the asset-based carriers that act as a conduit between buyer and seller. The supply chain is comprised of trains, highways, air, and sea transportation. These asset-based carriers lease ships and planes that are extensively employed for international transportation of large and wholesale commodities.
- 3PL- Logistics Service Provider: This is when information becomes a bit more inclusive. 3PL logistics, or third-party logistics, is the most prevalent model in commercial transportation. As with the 2PL model, it entails the transportation and administration of all services performed; however, it also includes additional services. They include inventory management and warehousing, labeling, product packaging, customs brokerage, and information technology services such as tracking items and determining delivery status.
- 4PL- Supply Chain Overseer: Where 3PL logistics becomes inflexible, 4PL logistics takes over. The range of services provided by 3PL is also included in this model, with the exception that transportation operations and inventory control are also outsourced to the logistics solutions provider. In 3PL logistics, the seller or manufacturer is responsible for operational management. In 4PL Logistics, on the other hand, the solutions provider manages the complete supply chain.
- 5PL- Solution Optimizer Services- 5PL Logistics expands a logistics service provider’s service index. Along with the duties associated with 3PL and 4PL logistics, the seller receives a framework for prudent planning and implementation of various supply chain segments. These parts cover the acquisition of inventory, services, data, and the flow of capital required for transportation planning, delivery, and tracking.
According to the United States Department of Labor, a logistics manager is responsible for supervising the acquisition and delivery of items within a supply chain (DOL). They play a critical role in ensuring that clients receive their merchandise.
Transportation is the movement of things, whereas logistics is the management of inbound and outbound transportation of goods from the manufacturer to the end user. Transportation logistics is concerned with transporting goods and services from one point to another.
From a product’s place of origin to its point of consumption, global logistics links crucial supply chain components.
Free Online Certification Courses in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
There is a variety of free logistics and supply chain management courses available to educate you on how to improve the flow of products and services. Short certificate courses like Introduction To Supply Chain Management or Introduction To Supply Chain Design are recommended. Both of these courses will explain all of the fundamentals and benefits of a strong supply chain. Longer diploma courses, such as Diploma in Supply Chain Management, which is a thorough guide on the subject, are also recommended.
Logistics Courses Near Me
Those interested in working in product placement and distribution frequently undertake logistics courses. Online, remote learning, and classroom education are all offered as alternatives for certification, diploma, and degree programs. You can also pursue retail and logistics management course or one of the shipping and logistics courses.
Product distribution, transportation management, supply chain, inventory control, and customer service are all subjects covered in logistics classes. Freight and products, warehouse distribution, transportation management, retail management, product design, and other goods and services related occupations are common for graduates of logistics programs.
Those interested in working in product placement and distribution frequently undertake logistics courses. Online, remote learning, and classroom education are all offered as alternatives for certification, diploma, and degree programs; Logistics courses qualifications vary among institutions.
Importance of logistics
Although logistics is focused on the transfer of commodities, importance of logistics are far-reaching. In the corporate world, logistics success leads to higher efficiency, reduced costs, higher production rates, better inventory control, wiser warehouse space utilization, enhanced customer and supplier satisfaction, and a better customer experience.
What is the importance of distribution management? Distribution management is primarily concerned with coordinating everything involved in getting goods to the consumer in a timely and waste-free manner. As a result, it has a direct bearing on profitability.
Optimizing procedures to optimize profits, reduce manual labor, make educated choices, and meet customer expectations are all benefits of logistics management. Other importance of logistics management include increased customer satisfaction, improved efficiency, visibility and cost-savings.
The major importance of logistics in supply chain management is to enhance the overall value of each delivery, as measured by customer satisfaction. This means that human resource reduction and optimization must be linked to maintaining a particular degree of quality customer service.
Marketing logistics guarantees that organizations collaborate and generate the marketing materials necessary to sell a product effectively. Marketing logistics helps a business to streamline interactions between the logistics provider and the client.
Advantages of logistics include increased efficiencies , lower costs, higher production rates, better inventory control, smarter use of warehouse space, increased customer and supplier satisfaction, and an improved customer experience.
Distribution Management Concept
The process of organizing the movement of goods from the supplier or producer to the point of sale is called distribution management. It is a catch-all term that encompasses a range of activities and operations, including packaging, inventory management, warehousing, supply chain management, and logistics.
Distribution management is a critical component of distributors’ and wholesalers’ business cycles. Profit margins for firms are contingent upon their ability to turn over their items fast. The more they sell, the more money they receive, which implies the business’s future is brighter. It is also critical for firms to maintain a good distribution management system in order to remain competitive and satisfy consumers.
Distribution management is a procedure inside the supply chain that eventually results in the delivery of commodities to end users or customers. Distribution management is primarily about controlling the flow of commodities, whether from a wholesaler to a retailer or from a retailer to a customer.
Distribution management in marketing is the process of overseeing the transfer of goods from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler or retailer and eventually to the end customer.