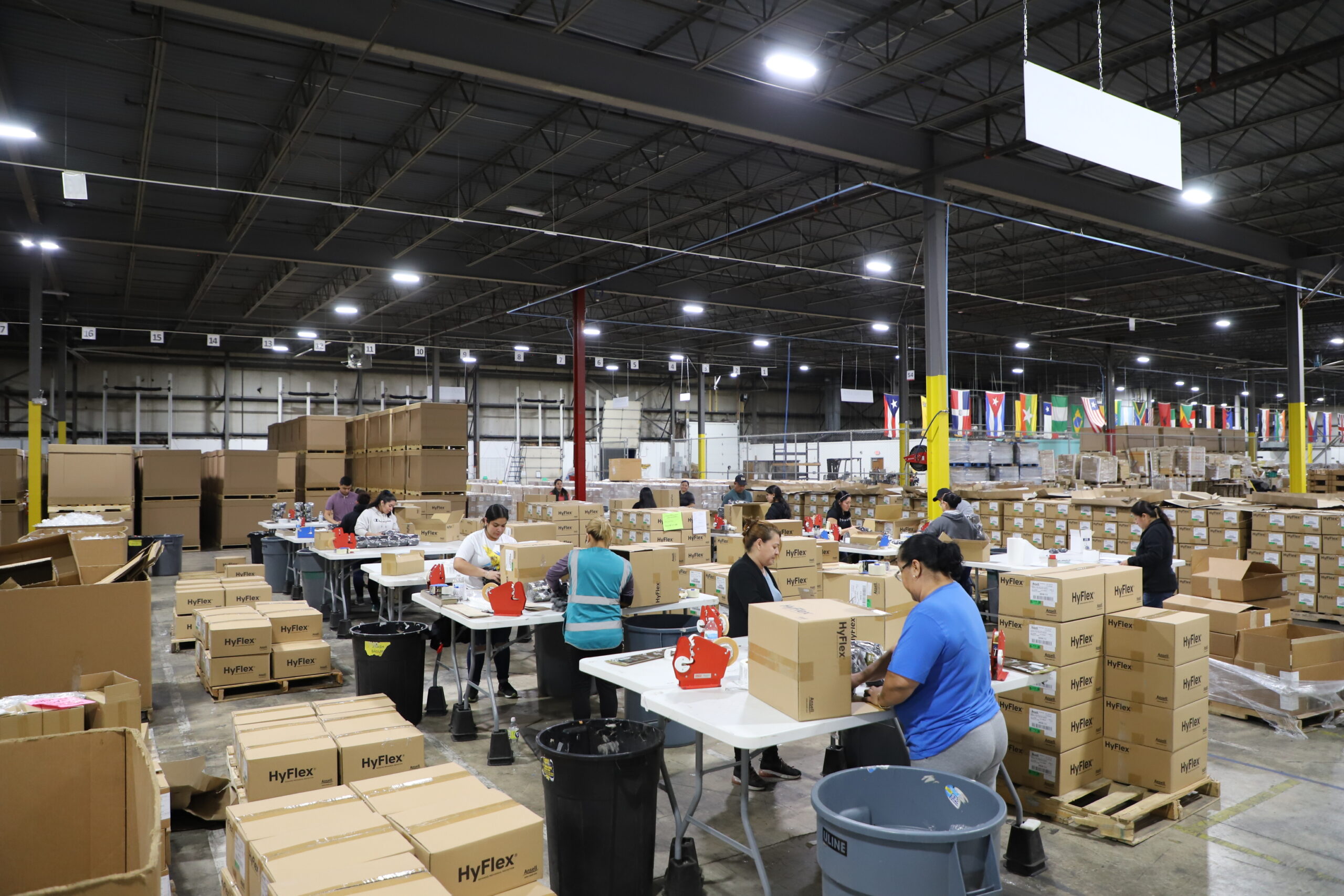
Partnering with Acción Performance allows your business to remain agile as production needs shift. Our custom logistics returns good handling strategies eliminate wasted resources by optimizing performance as we seamlessly integrate into your logistics processes.
Logistics Returns Good Handling
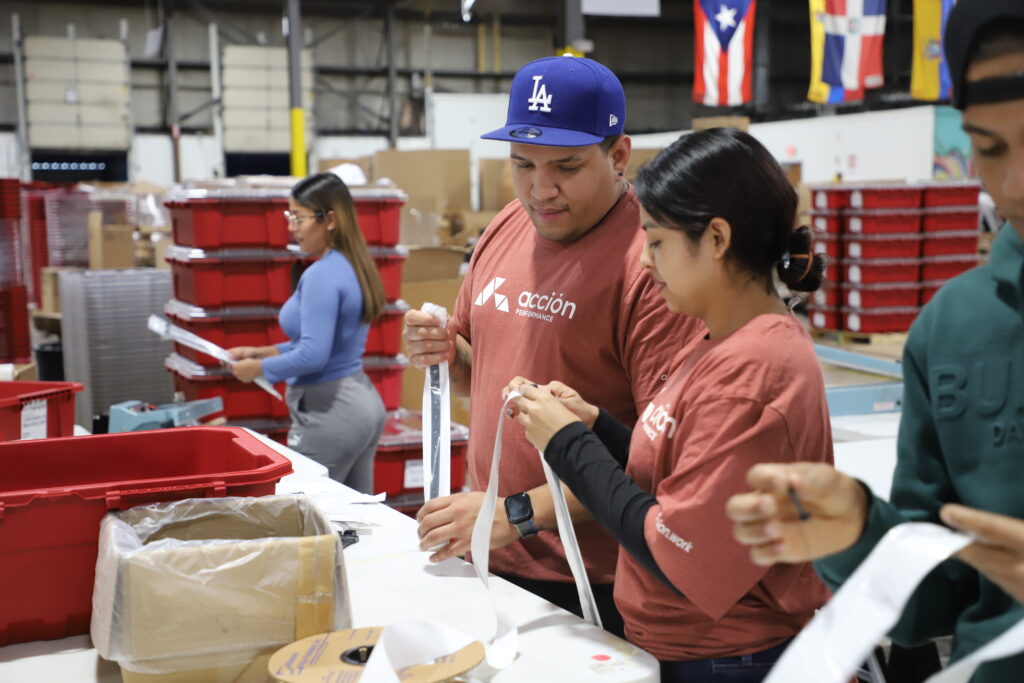



Packaging Solutions
Stay on top of product alterations and capitalize on packaging as a marketing tool to your clients. Our team can focus on product appearance while ensuring safe and secure delivery to its destination.
OUR CAPABILITIES
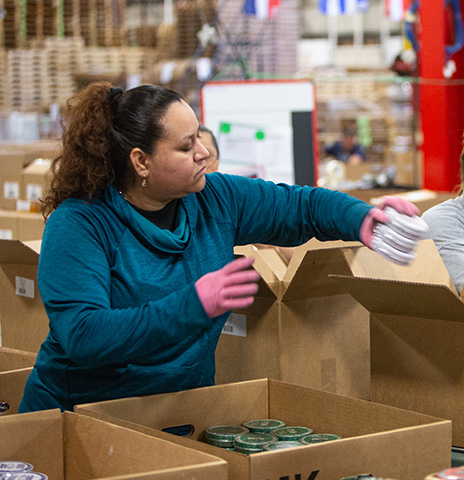
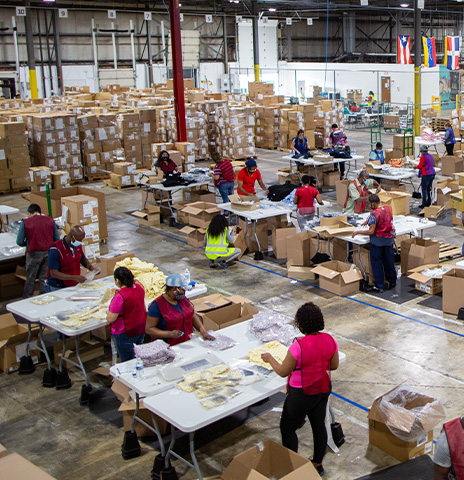
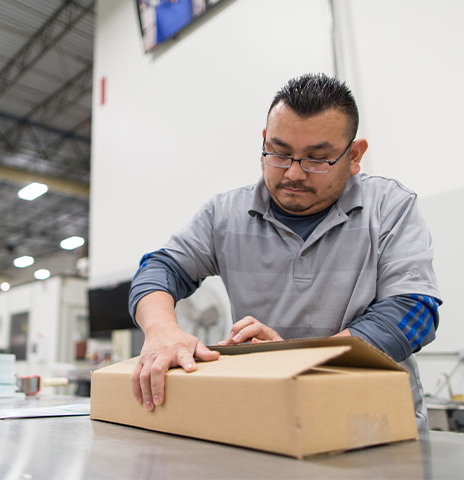



Fulfillment & Logistics Support
Improve efficiency and maintain client satisfaction by outsourcing key fulfillment operations. Our team leads will manage processes from pick and pack all the way to returns.
OUR CAPABILITIES
- Kitting and Assembly
- Primary and Secondary Packaging
- Shrink Wrap
- Labeling and Stickering
- Sortation
- Repack and Rework
- Display Builds
- Returns
- Refurbishing



Assembly & Co-Manufacturing Solutions
Reduce overhead costs and boost speed to market by shifting your assembly and co-manufacturing tasks to the Acción team. Our skilled team prioritizes quality and safety at every step.
OUR CAPABILITIES



Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) Prep
Ensure your products are properly packaged and sent on time for Fulfillment by Amazon. Acción Performance prepares your items to fit necessary requirements, saving your team extra time and valuable resources.
OUR CAPABILITIES
- Packaging Solutions
-



Packaging Solutions
Stay on top of product alterations and capitalize on packaging as a marketing tool to your clients. Our team can focus on product appearance while ensuring safe and secure delivery to its destination.
OUR CAPABILITIES
- Fulfillment &Logistics Support
-



Fulfillment & Logistics Support
Improve efficiency and maintain client satisfaction by outsourcing key fulfillment operations. Our team leads will manage processes from pick and pack all the way to returns.
OUR CAPABILITIES
- Kitting and Assembly
- Primary and Secondary Packaging
- Shrink Wrap
- Labeling and Stickering
- Sortation
- Repack and Rework
- Display Builds
- Returns
- Refurbishing
- Assembly & Co-Manufacturing Solutions
-



Assembly & Co-Manufacturing Solutions
Reduce overhead costs and boost speed to market by shifting your assembly and co-manufacturing tasks to the Acción team. Our skilled team prioritizes quality and safety at every step.
OUR CAPABILITIES
- Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) Prep
-



Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) Prep
Ensure your products are properly packaged and sent on time for Fulfillment by Amazon. Acción Performance prepares your items to fit necessary requirements, saving your team extra time and valuable resources.
OUR CAPABILITIES
Our Capabilities
Don’t let capacity constraints keep you from reaching your operational goals. Acción Performance can quickly adjust our resources to get started on projects quickly, and exceed timeline expectations.
Managing Modern Solutions
Optimized supply chain solutions aren’t “one size fits all,” and neither are our pricing models. Our team
finds the best approach for your project to maximize your resources, including cost.








Custom Solutions
See how the Acción team creates individualized solutions for our clients across industries to optimize their unique demands.
Logistics Returns Goods Handling
Logistics Return Goods Handling is the method of returning goods to the manufacturer, retailers, or third-party liquidators if the product specification is not met or if the actual product varies from the perceived product. Online purchasing has led to an increase in logistics return goods handling which is good for a customer but though manufacturers and retailers are happy to have goods returned it discredits the manufacturer and decreases money invested into a product
Reverse Logistics companies are ShipBob, XPO Logistics, Bowman Logistics, Mercury Logistics, Optoro, Zipline Logistics. When done correctly, it can improve customer experience, increase efficiency and revenue, and decrease wastage.
Reverse logistics examples occur:
- When goods are returned by customers
- Unsold goods are returned as per contract by distribution partners
- Packaging re-use occurs
- Goods are refurbished
- When guarantee agreements provide for repairs and maintenance
- Returned or defective goods need re-manufacturing
- Secondary market selling due to returns or overstocking
- End-life goods are recycled and disposed of.
Companies that can serve as reverse logistics examples are Apple, UPS, H&M, and Dasani.
The reverse logistics process entails returns, recalls, repairs, repackaging for restock or resale, recycling, and disposal where returned goods can be re-used in the manufacture of new products.
Benefits of Reverse Logistics
The benefits of reverse and challenges of reverse logistics are:
Benefits:
- Leads to a better ROI and decreased costs as costs are being recouped along the system thus increasing profit margins.
- Increased customer satisfaction leading to return customers
- Reduces waste as goods are identified and utilized for re-use, re-selling, or recycling thereby increasing the brand’s social and environmental responsibility image greatly.
- Opportunities for consolidation and return avoidance impacts less on the environment when transportation is reduced at every opportunity.
- Reduces losses and unplanned revenue costs
- Fosters a culture of industry leadership
Challenges:
- The high cost of reverse logistics.
- The rationale of returns is inexplicable and unpredictable.
- Products returned are viewed poorly.
- A shortage of labor resources to handle the returns adequately and efficiently.
The benefits of reverse logistics in supply chain management cannot be overemphasized. Not only will your supply chain management system be more transparent but you will be able to track a product’s life cycle, improve inventory management, identify and improve forward and reverse supply chain processes. This will lead to increased productivity, faster supply times, increase effectiveness, reduce supply chain risks and cost and lead to greater customer satisfaction.
On the whole, logistics does not have a favorable image when it comes to sustainability. The benefits of reverse logistics to the environment is one area where this is not the case. Repairs, refurbishment, repackaging, recycling, and the harvesting of materials during these processes reduce not only the environmental impact but also its social impact. Unnecessary transportation processes can be reduced by an effective logistics operation which ultimately reduces carbon emissions and improves air quality at minimal financial and environmental costs to the company. The benefits of reverse logistics can also be beneficial to the company’s profitability and use of assets.
Apple Reverse Logistics
Apple was a top supply chain supplier for three years running in 2008 largely due to its reverse logistics and reverse management processes and procedures. Apple offers discounts to customers when turning in their old devices. These devices are reversed logistics back to the factories and good condition and usable parts are reused in newer products.
For Dell reverse logistics has created a profit source from refurbished parts that are sold externally through a broker or is sold internally. This process led Dell to discover that at times the parts were more valuable than the source and gave it a new direction to move in. Dell, Matt Snyder of Dell has said the goal is to “increase revenue-generating opportunities while decreasing operating expenses,”
H&M reverse logistics is an initiative by the Swedish company to make fashion more sustainable. By including both consumers and suppliers H&M aims to have a climate-positive value chain that amongst other focuses on its distribution activities.
H&M sustainable competitive advantage stems from its business concept of delivering quality fashion at the best price to all concerned in a sustainable manner. This sustainability is non-compromisable and is a key business concept driving force.
Reverse Logistics Warehouse
The role of the warehouse in reverse logistics is critical. As the processing site, the value of all products going through it is maximized. The warehouse receives and evaluates unwanted goods. It is then processed by restocking if in a good condition to be sold at normal price. It can re-package the returned goods to be sold at full price. If these options are not viable it can try and recover as much of the cost of the product as possible by returning the goods to the supplier, disposing of it in an environmentally safe manner or selling to staff, or giving to charities. At times it is the reverse logistics warehouse task to credit a customer’s account when goods are returned.
The types of reverse logistics entail:
- Returns Management
- Returns policy and procedure (RPP)
- Returns avoidance
- Remanufacturing
- Refurbishing
- Packaging
- Unsold goods
- End-of-life and
- Delivery Failure
- Rentals and leasing
- Repairs and maintenance:
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Reverse Logistics
The advantages and disadvantages of reverse logistics are that it has minimal impact on the environment, it improves customer satisfaction and loyalty while improving the company’s corporate image as a company willing to take back goods that are unwanted or faulty, creates a new income stream which recovers some of the cost if not all of the product, leads to a far better stock control management system. Manpower, times, and costs can be more valuable when returned goods are mined for usable parts than it would have been had new materials been used. The effect of these advantages is that costs are minimized while revenue is optimized as best as possible.
The disadvantages of reverse logistics are :
- Loss of control especially if third-party outbound logistics is used.
- Unaccouccounted costs such as labor costs
- Fulfillment times are longer owing to the added burden on the system
- Returned goods have specific transportation, handling, storing, maintaining, and accounting requirements
- Gaining a competitive edge is difficult to achieve in an industry rife with near competitive parity
- Not all companies may be adapt at handling reverse logistics as they are forward logistics
History Of Reverse Logistics
The history of reverse logistics can be traced back to American Civil War. General William T. Sherman realized that the success of his operations were reliant on a reliable supply to his soldiers while moving through hostile territories. In 1892 Montgomery Ward, an American Furniture company refunded a customer’s purchase in full if they were not fully satisfied with their purchase. During WWII shortages in materials led to the rebuilding of automotive parts. This continues today with 95% of starters and alternators being sold are remanufactured. The Tylenol scare of 1984 had McNeil Laboratories remove and replace tainted products in next to no time restoring faith in the company and setting new standards for reverse logistics. In 1991, The Federal Republic of Germany passed recycling ordinances in 1991 which paved the way for the UK to require shippers and manufacturers to return and recycle packing materials in 1996. In 2001 the European Union mandated a 50-65% recovery of packaging and recycling waste which led to compliance by many countries wanting to do business with the EU.
The importance of reverse logistics is necessary for the maintenance of an efficient flow of goods which reduces costs, creates value, decreases risk, and completes the product life cycle. It increases sales and profits, uplifts the image of a business, and creates an overall image that is positive for the company.
importance of reverse logistics in supply chain management
international reverse logistics as practiced by Zara, Apple, etc is the practices and processes needed to be implemented to get a product from the end-user back to the manufacturer to dispose of it in the most efficient and cost-effective way possible whether it be by repairing, recycling, refurbishing, re-manufacturing or scraping the product.
reverse logistics in supply chain management
An introduction to reverse logistics to fully understand what reverse logistics is follows hereunder.
The General Council Of Logistics Management defines reverse logistics as “is the process of implementing, controlling, and planning the cost-effective flow of finished goods, raw materials, and in-process inventory. The flow is from the point of consumption (i.e. the customer) to the point of origin (i.e. the manufacturer), to properly dispose of these or to recapture value.” It refers to returned goods, the recycling of packaged materials, the disposal of previously sold items, refurbished, re-manufactured goods, etc which return inwards to the supply chain.
Reverse Supply Chain Examples
- Returns Handling occurs when customers return goods still under warranty.
- Returns Avoidance Processes attempts to reduce returns through support portals or repair partners.
- Remanufacturing uses used, repaired, and new parts in the making of new products.
- Refurbishing
- Reconditioning used goods to be resold.
- Packaging material is returned inwards to the supply chain eg bottles
- Unsold Goods are returned as per agreed terms to distribution partners
- End-of-Life Accepting where goods that are no longer usable are returned for reuse or recycling.
- Delivery Failures occurs when customers refuse acceptance of delivery.
- Rentals & Leasing occurs when rental goods are returned
Types of reverse logistics pdf
what is reverse logistics in supply chain management
Zara reverse logistics model relies heavily on digitization of POS data, social media posts and website clicks, IoT technology, GPS cloud computing, and advanced analytics to manage its reverse logistics processes. Zara relies heavily on real-time data to drive all its processes. Its central distribution is a vital cog in the entire supply chain process with all goods being returned to Spain before being shipped elsewhere.